As of writing, the crypto market stands at a valuation of $1.800 trillion. What that means is that it is equivalent to Brazil's GDP which is currently sitting at the top 9 amongst other countries.
What is more commonly perceived of the crypto market is it is either a free money-generating industry or a world where scammers are lurking.
It is more than that - more than just JPEG marketplace, trading opportunities & interesting terms.
Where do we start?
The evolution of the Internet has made a lot of the technology we are using today possible. Some of the techs we have been using daily like WhatsApps services are not possible 20 years ago during the Web 1.0 version but it has become an essential tool for us today as Web 2.0 makes it possible.
Web 2.0 has brought huge changes to how we live, work & interact today. Now, imagine what would happen with Web 3.0, where users will be empowered - to own, verify & interact seamlessly.
What’s exciting with Web 3.0 is the rapid progression & emergence of projects within the space. Whatever we are familiar with right now within Web 2.0 space, that we are using on daily basis, you can expect a project has been built or is being built in the Web 3.0 space.
How the Web 3.0 changes the way we do things?
We have read about the infamous news of Donald Trump getting his Twitter account suspended despite the irony of him at the helm holding the position as the President of the United States (POTUS) back in January 2021. The fact that he is, at that time, the most powerful person as POTUS does not deter Twitter at all from pushing forward such action, perhaps in the name of equality but at the expense of freedom of speech.
Web 3.0 will be vastly different than Web 2.0 in the sense that no one can pull such an act (account banning for example) on another person, even if the order came from the President of the United States. That is how an ideal decentralization of Web 3.0 would work.
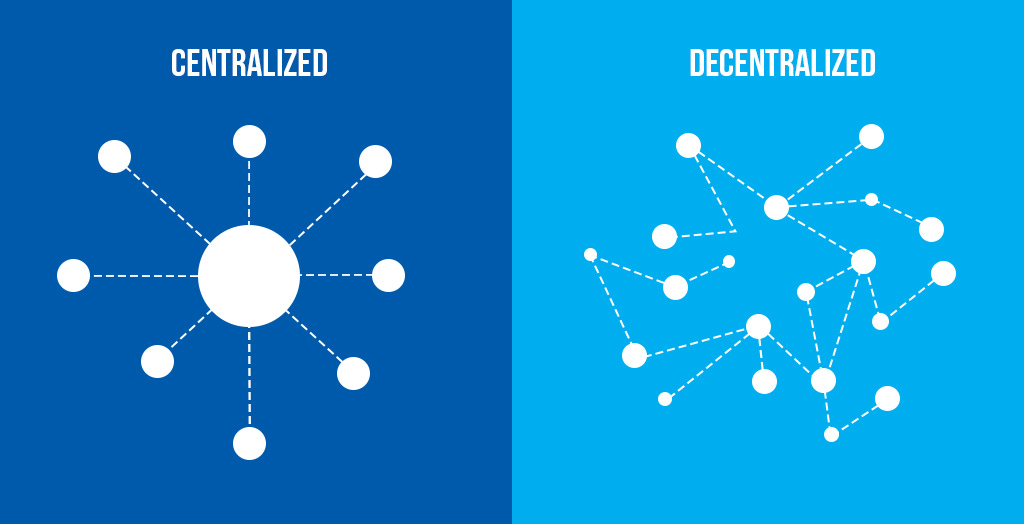
For this concept of decentralization to work, where everything is available in public yet no one can change or amend anything, it boils down to the foundation of crypto i.e blockchain.
Most of the websites, apps that we are using right now are mainly hosted on cloud servers. While operationally, it makes sense in terms of cost & resources utilization, the issue looms in the area where there is an overreliance on a single company to ensure their websites/apps run smoothly all the time.
This is exactly what has happened to Meta services where all Facebook, Instagram & WhatsApp faces outage for 7 hours long and a recent disruption that happened to Spotify & Discord would give a sense of how much reliance we are on these cloud services.
Though we have not been hit by the disruption issue too often, understanding the idea that these companies have such a huge amount of power should scare you a little.
The concept of how cloud servers function serves as a similar analogy (albeit a simplified version) for how blockchain works. It is the foundation for most of the applications of Web 3.0 to be built onto. Of course, given that blockchain empowers Web 3.0, here are the unique traits:
No one owns blockchain. It is public.
It is transparent - any transactions that occur on it, everyone can see it yet no one can make any amendment to it.
Higher privacy - each user can organize, sort & manage their data
Higher security - each user play an important role to enhance blockchain thus helping to secure blockchain in a complex manner that is deemed impossible to hack into the system
The true wonder lies on the foundation of blockchain that it is public & transparent yet secure. This is only possible with the main two contributors i.e. miners & token stakers.
Miners & token stakers contribute to blockchain in different manners. The two consensus mechanisms below address the contribution of miners vs token stakers.
Proof of Work or POW (contributor: Miners)
The largest & pioneer blockchain, Ethereum & the largest cryptocurrency, Bitcoin use this method to ensure Ethereum & Bitcoin transaction is secured. Proof of Work works in the way that we often hear in the news of illegal crypto or Bitcoin mining. We see loads of computer CPUs get carried away from the site.
POW is the culprit of:
Illegal mining where miners steal electricity due to the large amount of electricity required to mine
Large energy consumption is required to mine hence it is deemed as non-environmental friendly
The underlying principle of how POW works is that miners would need high-performing hardware to solve difficult cryptographic puzzles. By being the first to solve them, miners would be rewarded with the token - in this case, Ether token for Ethereum miners & Bitcoin for Bitcoin miners.
2. Proof of Stake or POS (contributor: Token Staker)
Proof of Stake changes the way how the blocks or transactions within the blockchain are verified. Instead of relying on the high processing power of a CPU, validation happens when a validator locked their token as collateral to be used as validation. In return, validators gain a return from the token they staked, taking a pie of the transaction fees that happen on the blockchain.
POS is used by Cardano, Avalanche, Polkadot & Solana, to name a few. This addresses the high transactional fees imposed by the Ethereum blockchain & the large energy consumption by the miners.
There are other new consensus mechanisms out there like Proof of History, Proof of Burn, Proof of Authority to name a few (and perhaps more may emerge soon) but the main ones are still the Proof of Work & Proof of Stake.
51% Rule
These two consensus mechanisms seem complicated but there is a principle that beholds these blockchains. Perhaps you have heard of Kickstarter or Crowdfunding. It is a similar concept wherein the case with POW or POS, it is the utilization of peer-to-peer validation on blockchain to ensure the security of the system in return getting tokens as a reward for their work.
With the need of many various validators to confirm & backed the validity of transactions, it is almost impossible for hackers to hack into the system unless they have 51% of the total token (in POS case) or computing power (in POW case). In the case of Ethereum, it is impossible to accumulate all of the 51% of Ether tokens & a total of 51% computing power to gain such leverage given that Ethereum is valued at $305 billion as of writing. This is known as the 51% Rule.
However, the same cannot be said for smaller or newer networks where it is significantly easier to gain that kind of leverage, allowing scammers & hackers to be at play.
Fees Mechanism
Although Ethereum has a vast majority of the projects running on top of its system, it is famously known to have extremely high gas fees, 7 times more expensive than Avalanche (as of 27th September 2021, based on the below), and low transaction speed.


Perhaps a depiction of a real-life case scenario shown below would provide a better idea of how users with low capital would need to bear high transactional fees which makes it less friendly among the mass user.

On top of that, high energy consumption in the mining process causes a lot of people to reject it, due to environmental concerns.
This puts Ethereum at a huge disadvantage but being a pioneer in the blockchain world, Ethereum is a more secure choice as a blockchain to be built upon compared to other new Ethereum competitors (aka known as Ethereum Killers) as it has been proven historically as a secure & safe blockchain, with high adoption from various projects.
Why companies are not jumping onto the bandwagon yet?
That said, although blockchain is definitely the next big thing (akin to the hype surrounding the Internet during the earlier 2000s), there are a few barriers that stopped most companies to invest in it right now.
High cost & high complexity in setting up for both the organization & for users. The new system indicates the organization needs to adopt a totally new system & have a strong tech team with expertise in blockchain & crypto tech.
Lack of control over a few key aspects that an organization predominantly has ultimate control over like data, changes to the system, users. The fast-evolving blockchain trend may render today’s system built unusable, causing huge uncertainty to the organization.
Relatively low user adoption for the mass market.
Perhaps we will be seeing more and more companies investing & adopting blockchain once some of the issues above (especially cost & user adoption issues) are tackled.
Evolution of Blockchain since 1991
Blockchain has come a long way since 1991 & all the case studies we have seen today are made possible with the introduction of blockchain and all the innovation that comes with it.
Although there are a lot of benefits from having blockchain, it comes down to utilization & how it helps to drive the next things that would help improve our livelihood.
Disclaimer: I am, by no means an expert in tech or crypto. This serves as an outlet for me to learn & capture my thoughts, knowledge & the key essence of it in a simplified manner.
My personal experience in trying to get more involved in the crypto market has made me realize how most of the resources available are either too technical or full of jargon. That creates an unnecessary barrier to most of the beginners out there who are trying to grasp the idea of crypto & understanding what’s happening within the circle.
That, in turn, has created the need for me to share what I have learned through Untangling the Knots - in a simple & digestible manner.